Orthopedic surgery has traditionally relied on human skill, careful planning, and execution by experienced surgeons. While these factors have achieved remarkable success, artificial intelligence (AI) and robotics are now transforming the field. Technological advancements in orthopedics are offering precise surgical outcomes, faster recovery times, and improved patient satisfaction like never before.
This blog explores the impact of AI and robotics in orthopedic surgery, their advantages, and the implications for patients.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Orthopedic Surgery
AI refers to computer technology capable of analyzing data, recognizing patterns, and predicting outcomes. In orthopedics, AI is applied in several areas:
- Preoperative Planning and Imaging
AI algorithms can analyze X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans to detect fractures, degenerative disease, or alignment problems. By reviewing thousands of images, AI assists surgeons in developing precise preoperative plans, including implant type, alignment, and surgical challenges.
Keywords: AI in orthopedic surgery, AI preoperative planning, AI imaging analysis
- Predicting Surgical Outcomes
Machine learning algorithms can predict recovery time, risk of complications, and joint functionality, helping surgeons and patients make informed treatment decisions.
- Personalized Treatment
AI processes patient-specific data such as age, weight, bone density, and lifestyle to tailor surgical options for each individual, ensuring a more effective and personalized approach.
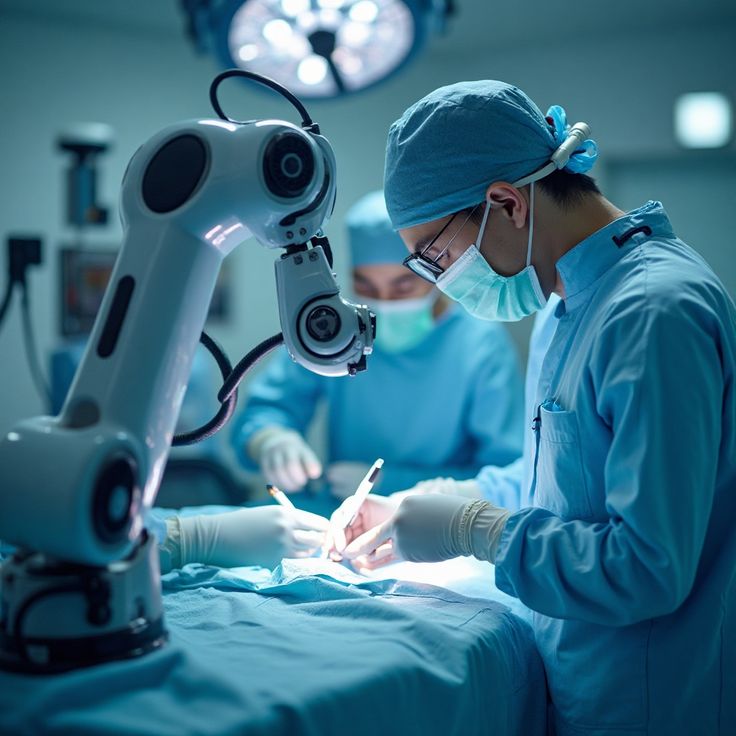
The Importance of Robotics in Orthopedic Surgeries
Robotics enhances accuracy, reliability, and minimal invasiveness in orthopedic procedures. Robots assist surgeons, combining human experience with technological precision.
- Robotic-Assisted Joint Surgery
Robotic systems are widely used in knee, hip, and shoulder replacements, offering:
- Accurate bone cuts
- Proper implant placement and alignment
- Less soft tissue damage
- Easier post-operative healing
Patients experience reduced pain, improved mobility, and longer-lasting joint replacements.
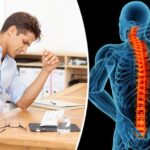
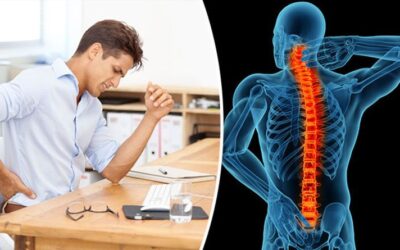
- Spine Surgery and Robotics
Robotic guidance ensures precise insertion of screws, implants, and intervertebral devices in spine surgeries, reducing the risk of nerve damage and complications.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures
Robotics allows surgeons to use smaller incisions, reducing bleeding, infection risk, and hospital stays, while enabling faster recovery for patients.
Keywords: robotic orthopedic surgery, joint replacement using robots, minimally invasive orthopedic procedures
Benefits of AI & Robotics in Orthopedics
- Increased Precision and Accuracy
AI and robotics minimize human error, particularly in procedures requiring millimeter-level accuracy.
- Enhanced Surgical Planning
AI provides data-driven insights, helping surgeons plan procedures more effectively and safely.
- Faster Recovery Times
Robotic-assisted surgeries typically cause less post-operative pain and enable quicker recovery.
- Improved Long-Term Outcomes
Precise alignment and execution reduce wear and tear, increasing the longevity of joint replacements.
- Real-Time Assistance During Surgery
Robotics provides real-time feedback, allowing surgeons to make immediate adjustments, enhancing patient safety.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the benefits, AI and robotics in orthopedics present certain challenges:
- High Costs: Robotic systems and AI infrastructure are expensive.
- Learning Curve: Surgeons require training to effectively use these technologies.
- Technology Dependence: Human oversight is essential to avoid errors in judgment.
Nevertheless, hospitals are increasingly adopting these technologies due to their precision, efficiency, and positive patient outcomes.
The Future of Orthopedic Surgery
The integration of AI and robotics is only the beginning. Future possibilities include:
- Fully autonomous robotic-assisted surgeries for routine procedures
- Real-time AI monitoring of patient vitals during surgery
- Predictive analytics for post-operative care and physical therapy
- International data networks to optimize surgical methods and outcomes
These innovations promise safer, more efficient, and patient-friendly orthopedic care.
Conclusion
Artificial intelligence and robotics are revolutionizing orthopedic surgery, enhancing precision, reducing complications, and improving recovery. As these technologies advance, patients can expect quicker, safer, and more personalized treatments. For individuals awaiting orthopedic procedures, exploring AI and robotic-assisted options may offer a glimpse into the future of joint and spine care.